What is DMARC Alignment?

Reading Time: 8 min
DMARC alignment ensures that the domains in different sections of an email header match during authentication checks. This process is key to verifying whether an email is legitimate and originates from an authorized sender. If an email aligns with either SPF or DKIM, it meets DMARC alignment requirements and is considered authentic.
By enabling DMARC alignment, organizations strengthen email security, preventing phishing, spoofing, and other forms of email fraud.
Secure Your Email
Stop Email Spoofing and Improve Email Deliverability
15-day Free trial!
Latest Blogs
How to Add Your Logo to Gmail Emails: Gmail & Branded Emails
July 2, 2024 - 12:50 am
What Are the Cybersecurity Threats When Allowing Third-Party Cookies on Mac?
June 29, 2024 - 1:38 pm
DMARC: The Missing Link in Your MSP’s Defense Strategy
June 27, 2024 - 11:16 am
GoDaddy SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Record Configuration Guide: Step-By-Step
June 26, 2024 - 1:00 pm
How DMARC Alignment Works?
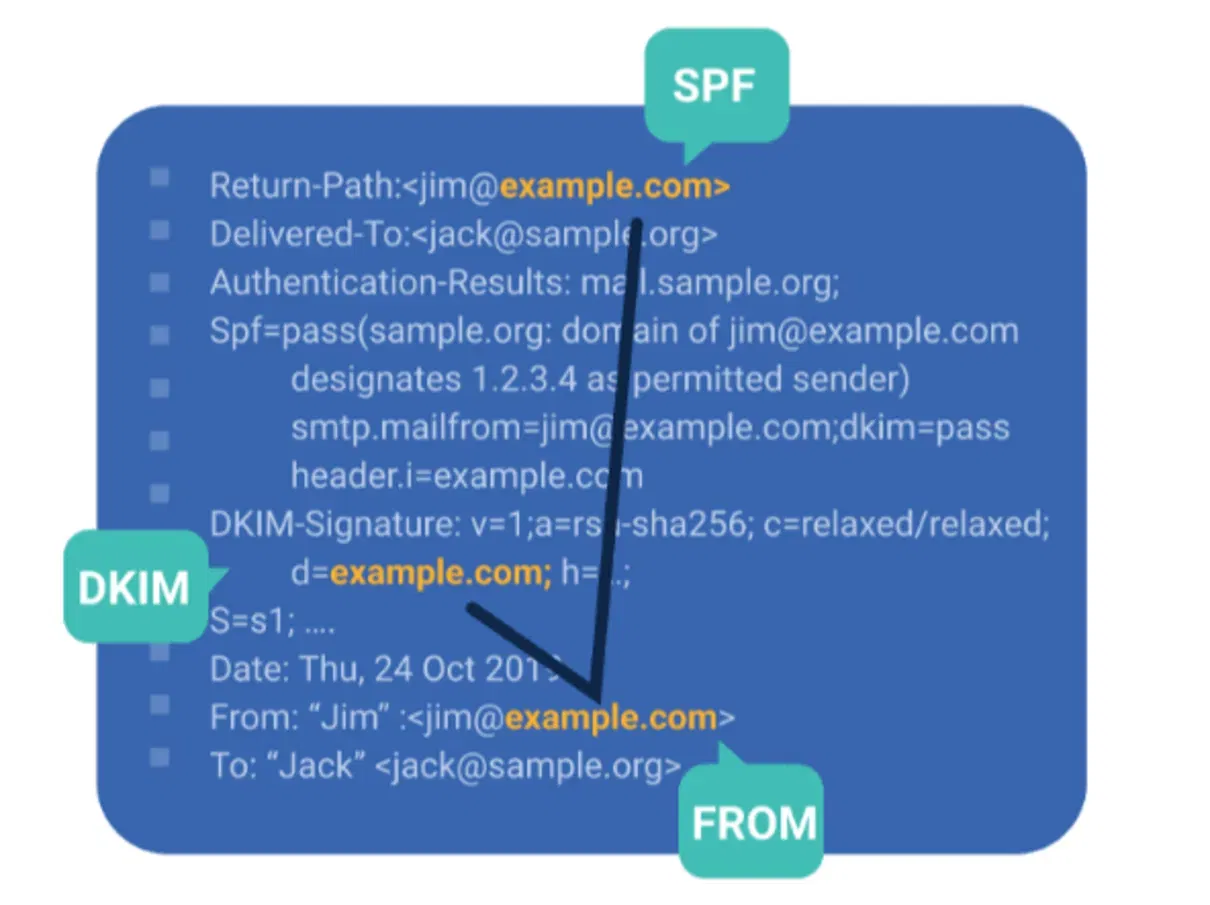
To determine DMARC alignment, email authentication protocols validate three key identifiers:
- From Header: The visible sender domain in an email
- Return-path address: Used for SPF validation
- DKIM signature Domain: The domain tied to the email’s cryptographic signature
If either SPF or DKIM aligns with the From header domain, the email passes DMARC authentication. Otherwise, it fails and can be rejected or flagged based on the domain owner’s policy.
The Role of SPF and DKIM in DMARC Alignment
Both SPF and DKIM play a crucial role in verifying email legitimacy
- SPF Alignment: Checks if the sending server’s IP matches the domain’s authorized sender list
- DKIM alignment: Uses cryptographic signatures to verify email integrity and authenticity
Organizations must configure both SPF and DKIM to achieve 100% DMARC compliance, ensuring maximum email security and preventing unauthorized senders from impersonating their domain.


Factors Affecting SPF and DKIM alignment
Several factors can cause alignment failures, including:
- Emails sent through third-party vendors that modify message headers.
- Forwarded emails, which may alter return-path addresses, breaking SPF alignment
Solution:
To maintain alignment, organizations should implement ARC alongside DMARC, SPF, and DKIM to handle forwarding issues and ensure uninterrupted authentication
Types of DMARC Alignment: Relaxed Vs Strict Modes
Organizations can choose between Relaxed or Strict alignment based on their security requirements:
1.DMARC Relaxed Alignment
- Allows subdomain mismatches- If the From header domain and SPF/DKIM domains share the same root domain, alignment is still considered valid.
- More flexible- Helps organizations using multiple email service providers and third-party senders.
- Lower false positives- Prevents legitimate emails from being rejected due to minor domain mismatches
Example: v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:[email@example.com](mailto:[email@example.com]); aspf=r; adkim=r
- aspf=r(SPF relaxed mode)- SPF alignment passes even if subdomains differ
- adkim=r(DKIM relaxed mode)- DKIM alignment passes with domain variations.
2.DMARC Strict Alignment
- Only exact domain matches pass- The From header domain must match SPF/DKIM domains exactly.
- Stronger security- Prevents spoofing attempts using subdomains
- Higher false positives risk-Requires precise authentication configuration to avoid blocking legitimate emails.
Example: v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:[email@example.com](mailto:[email@example.com]); aspf=s; adkim=s
• aspf=s(SPF strict mode)- SPF alignment passes only with an exact domain match
• adkim=s(DKIM strict mode)- DKIM alignment passes only when the signing domain matches the From header domain exactly.

Choosing the Right DMARC Alignment Mode
Organizations must consider security policies, email infrastructure, and risk tolerance when selecting an alignment mode:
Relaxed Alignment: Ideal for businesses using multiple third-party email providers, reducing email rejections.
Strict Alignment: Best for organizations requiring maximum protection against phishing and domain impersonation.
Monitoring Emails on Strict DMARC Alignment
To prevent email delivery issues with strict alignment, organizations should use a DMARC Analyzer tool. PowerDMARC provides
- Real-time monitoring of DMARC compliance
- Detailed reports on SPF and DKIM alignment failures
- Easy policy adjustments to improve authentication success rates.
Checking DMARC Alignment for Emails
Organizations can verify DMARC alignment using the PowerDMARC portal:
Steps to check DMARC alignment:
1. Log in to PowerDMARC
2. Navigate to DMARC Aggregate Reports under Reporting
3. Select per result to track compliance and alignment
DMARC pass; If either SPF or DKIM aligns with the from domain
DMARC Fail: If neither SPF nor DKIM aligns, indicating possible spoofing
Strengthen your Email Security with DMARC Alignment:
Key Takeaways:
- DMARC alignment ensures email authenticity by matching domain identities
- Relaxed alignment offers flexibility, while strict alignment provides stronger security.
- Using a DMARC analyzer helps monitor compliance and prevent authentication failures
